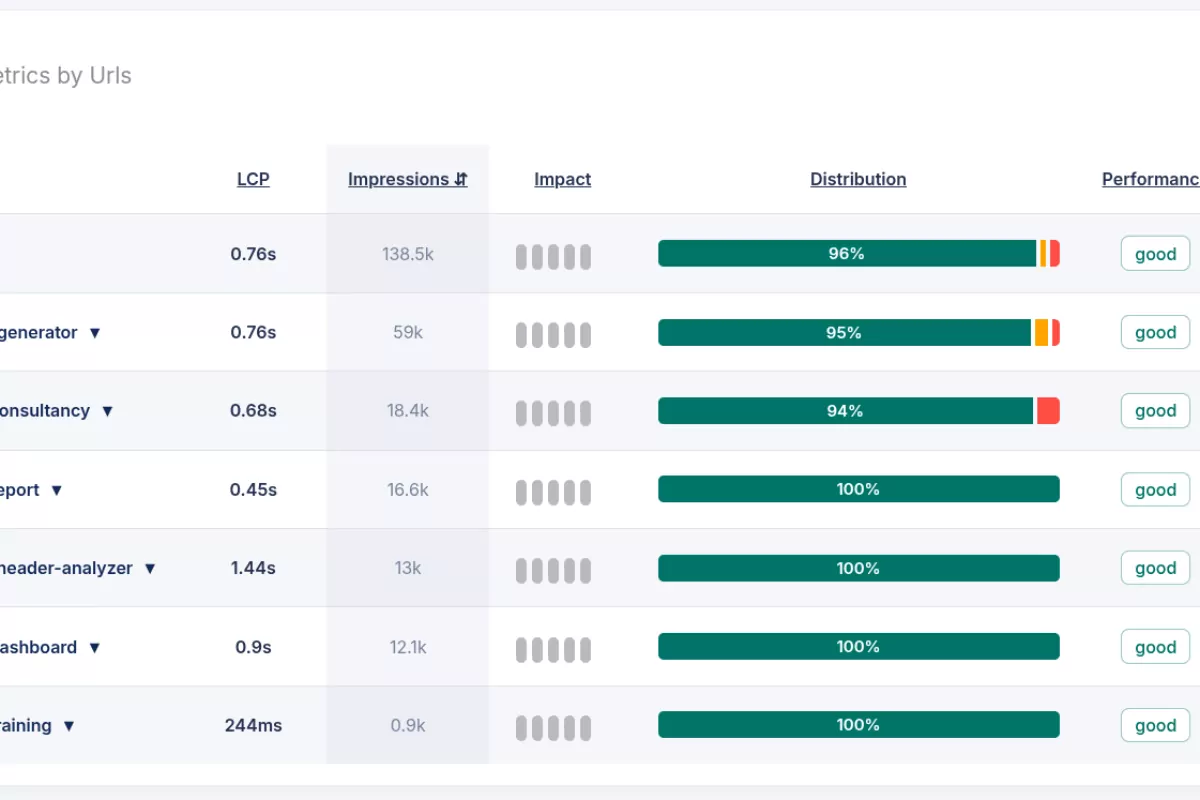
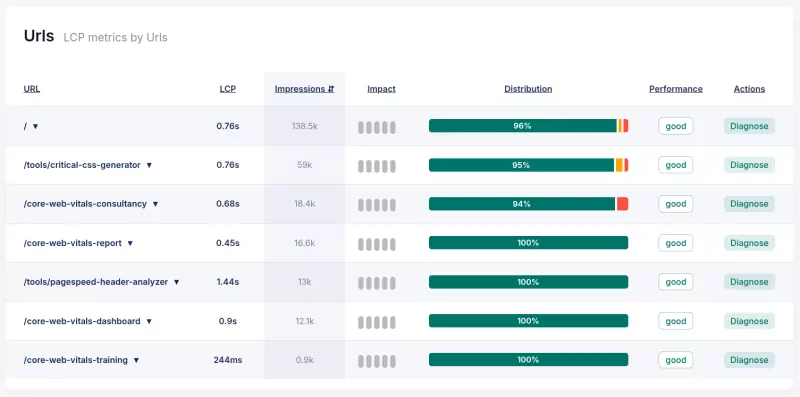
Core/Dash Dimension: Urls
Isolate and fix Core Web Vita;ls performance bottlenecks by specific Urls
Trusted by market leaders
Dimension: Page & Navigation: URLs (u)
The URL dimension isolates performance data for individual page paths. While Page Labels handle grouping, the URL dimension allows you to inspect the performance of exact addresses. This granularity is essential for optimizing critical entry points and high value pages.
Strategy by Scale
How you use the URL dimension depends on the size and architecture of your site.
- High Volume / Enterprise Sites: Focus on "Vital Pages." You cannot optimize every single URL manually. Use this view to monitor your most critical assets—your homepage, your highest converting landing page, or your primary checkout step. These specific URLs must perform flawlessly regardless of the broader template performance.
- Small / Marketing Sites: Focus on comprehensive coverage. With fewer pages, you can treat every URL as a unique application state. Monitor the entire sitemap to ensure no single page is dragging down your aggregate score.
Metric Specific Diagnostics
Each Core Web Vital behaves differently when viewed at the URL level.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Abnormally High LCP on a specific URL usually points to a unique asset issue. Check for a large, unoptimized hero image or video background that exists only on that page.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Layout shifts on specific URLs often indicate dynamic content injection. Look for ads, promotional banners, or cookie notices that load specifically on that page path.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Interaction delays on a single URL suggest heavy JavaScript execution tied to a unique feature. Investigate complex widgets like calculators, maps, or search filters found on that specific page.
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): If one URL has a significantly higher TTFB than others, it suggests a backend bottleneck. The database query for that specific content might be slow, or the page might be bypassing the cache.
Improving the Core Web Vitals by page
Use the URL dimension to execute precise, page-level optimizations.
- Sort by Impact: Sort the URL list by the Impact column. This identifies the individual pages where poor performance affects the largest user volume. Focus on the top URL first.
- Audit the Specific Page: Analyze the top URL for unique bottlenecks. Look for assets or scripts loaded specifically on this page, such as a homepage hero video or a landing page lead form, rather than shared template elements.
- Validate the Fix: After deploying an optimization to the specific URL, monitor its individual trend line. Confirm that the metric improves for that specific address before moving to the next URL in the list.
.